

Because it's assumed that the portfolio being evaluated is a diversified portfolio (meaning that the unsystematic risk has been eliminated), and because a diversified portfolio's main source of risk is the market risk (or systematic risk), beta is an appropriate measure of that risk. The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is used to determine a theoretically. The CAPM equation is used to identify the required return of an investment it is often used to evaluate realized performance for a diversified portfolio. Jensen’s alpha takes into consideration the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) and includes a risk-adjusted component in its calculation.Īlpha is computed in relation to the capital asset pricing model. The capital asset pricing model formula for calculating expected return is: The Capital Asset Pricing Model is used to forecast returns that can be obtained.The CAPM defines the price of financial assets according to the premium demanded by investors for bearing excess risk. It formalizes mean-variance optimization of a risky portfolio given the presence of a risk-free investment such as short-term government bonds. E (RM): Indicates the market asset’s predicted yield. Rf: Shows the return that is not dangerous. E (Ri): This shows the projected level of interest on a certain investment.
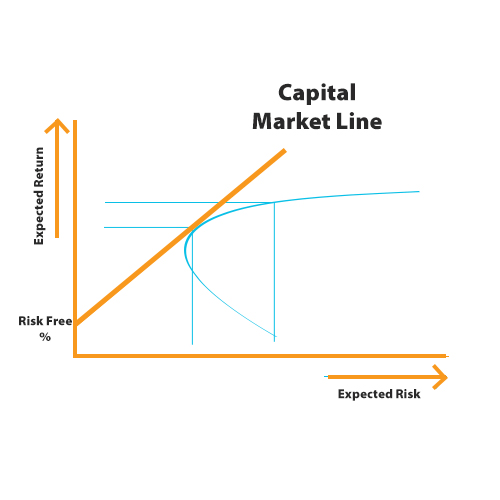
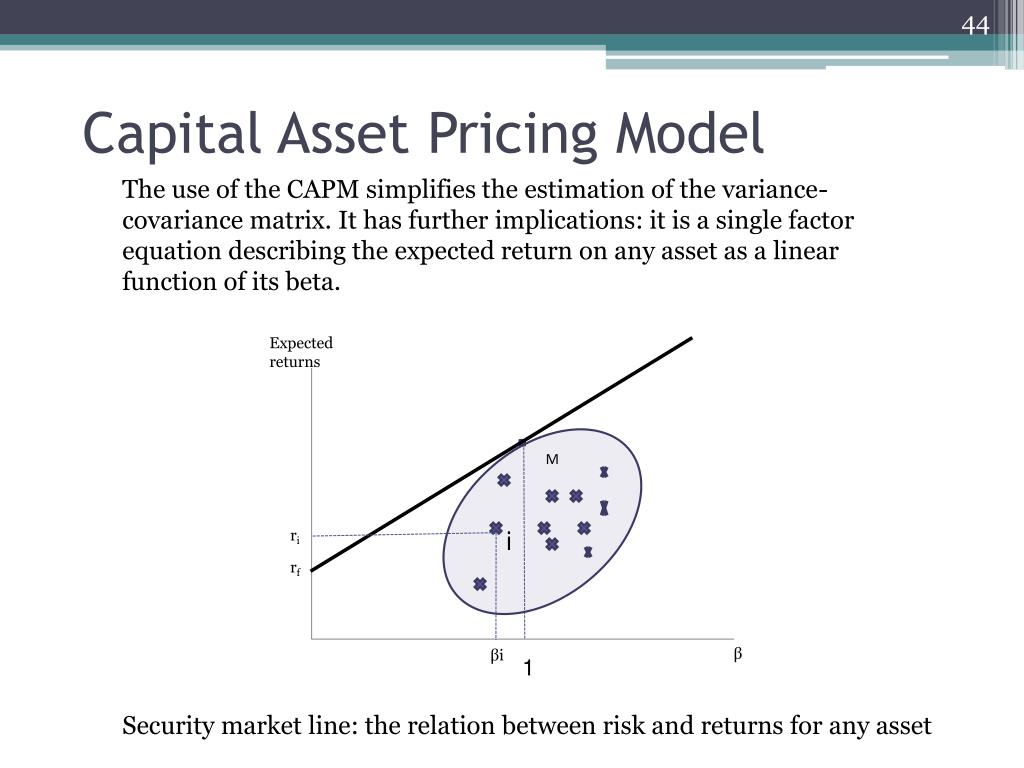
Because alpha represents the performance of a portfolio relative to a benchmark, it is often considered to represent the value that a portfolio manager adds to or subtracts from a fund's return. The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is an influential paradigm in financial risk management. The equation for the capital asset pricing model.Active portfolio managers seek to generate alpha in diversified portfolios, with diversification intended to eliminate unsystematic risk.Alpha refers to excess returns earned on an investment above the benchmark return.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
